Atopic dermatitis is the medical term for the most common variety of skin disorders known as eczema. Researchers still don’t really understand eczema — what causes it, why some people get it while others don’t, and why most children outgrow it but some suffer from it throughout their lives.
It can’t be totally random, though, because the prevalence of eczema is rising around the world, afflicting about 10% of children and young adults, and 2–5% of all people.
And while there are many treatments for eczema, including hygiene practices, identifying and avoiding personal triggers, and even corticosteroids, they don’t always work. And even if medicated creams work at first, sometimes people can develop tolerances to them with prolonged use, and more and more supplementary treatments may be required.
People in remission from eczema may dread their next relapse, and feel powerless to prevent their flare-ups. And as with most conditions that resist conventional medical intervention, people who suffer from long-term eczema may turn to alternative treatments, lifestyles, and diets.
But some evidence suggests that eczema may go hand in hand with food allergies. Food allergies are also on the rise, and researchers are paying special attention to the barrier function of the skin as it relates to allergic conditions. Might consuming certain foods increase the likelihood of both food allergies and atopic dermatitis? And might some foods protect against or reduce symptoms?
A man in Hong Kong allegedly cleared up his eczema on a largely plant-based diet. A woman’s severe eczema almost completely disappeared after she adopted a whole foods, plant-based approach. And another woman who had swollen eyes and flaking skin for 20 years saw her symptoms go away after four days of plant-based eating.
Are these isolated, idiosyncratic cases, or examples of the placebo effect? Or is it possible that a plant-based diet may really be helpful in the treatment of eczema, at least in some cases? After all, a quick search on Amazon reveals dozens of books on eczema diets, cleanses, detoxes, and other approaches — all of which claim success where mainstream medicine cannot.
In this article, we’ll explore the evidence for the claims that a plant-based diet, along with other lifestyle choices, can help relieve eczema suffering. First, though, let’s find out more about the disease — and what triggers it.
Understanding Eczema
As we’ve seen, eczema is also called atopic dermatitis. A quick peek at the etymology of the two words gives us insight into the disease. Dermatitis is inflammation of the skin, which can result in itching, flaking, swelling, oozing, and crusting. And atopic comes from the Greek words a and topos, which together mean “out of place” — i.e., unusual or strange.
In essence, eczema is a chronic condition that causes the skin to become itchy, dry, cracked, and inflamed. So basically, if your skin were a party, eczema would be that awkward guest who not only refuses to leave but also insists on playing the Macarena on repeat. It’s out of place and it definitely makes its presence felt!
In infants and young children, who are most likely to suffer from eczema, the areas typically affected include the face, the outside of the elbows, and the knees. In older children and adults, eczema generally appears on the hands and feet, the arms, and the back of the knees. We don’t know why the condition often migrates from one part of the body to another.
Another eczema mystery is what causes the disease. (The one thing we know for certain, and it’s good news, is that the condition isn’t contagious.) It can run in families, suggesting either genetic or environmental factors, and it often develops alongside other conditions, including asthma and hay fever.
Eczema so frequently occurs in tandem with allergies that there’s reason to suspect an immune system link. Just as allergic reactions appear to be the result of overactive and confused immune responses, eczema, too, may be the skin’s overreaction to harmless stimuli.
While there are some autoimmune conditions that affect the skin — including rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and dermatitis herpetiformis — eczema is not caused by the body attacking itself. Still, research shows that people with eczema are at higher risk of a number of autoimmune conditions, including alopecia, celiac disease, Crohn’s disease, rheumatoid arthritis, lupus, and ulcerative colitis.
What Triggers Eczema?
One of the most troubling aspects of eczema is the seeming unpredictability of the course of the condition. There are periods when the skin is clear and free of symptoms, called remissions, and times when it flares up.
It’s not entirely random, though. Certain things can trigger flares in susceptible people, including stress, environmental exposures, and food.
Stress and Eczema
We know now that stress is a lot more than a state of mind. Acute and chronic stress can cause big physiological changes throughout the body, including some that can trigger or exacerbate eczema. New understandings of the “brain-skin connection” point to the release of stress hormones, especially in large quantities or over an extended period of time, as sometimes fueling eczema symptoms.
As you can imagine (or may even know from personal experience), living with eczema is stressful in its own right, leading to a potentially vicious cycle in which stress triggers eczema, making it harder to sleep or relax, which in turn exacerbates the stress, and so on.
Research has shown that the skin immediately picks up on stress. What might be less obvious is that it’s also a target of stress responses.
As the largest organ of the body, the skin is one of the key sentries keeping track of the outside world for signs of threat. Specifically, the skin is an important barrier for immune functions, maintaining homeostasis between the external environment and internal tissues. When it’s working properly, the skin lets in the good stuff and keeps out the bad. With eczema, stress can weaken this homeostasis, increasing inflammation and immune function dysregulation.
Personal Care Products and Eczema
Exposure to certain chemicals and toxins in the environment may also trigger eczema in some people — which could partly explain why prevalence is on the rise.
It can be challenging for an individual to figure out what they’re sensitive to. And it may take time, focus, and an action plan to eliminate various exposures to see if doing so leads to any relief.
Some of the most commonly implicated exposures include personal care products, such as shampoos, conditioners, moisturizers, and other products that come into contact with the skin. Products that contain fragrances may increase itching, and those with sodium lauryl sulfate may irritate the skin of people prone to eczema.
Another category of eczema triggers includes fabrics. In particular, wool and some synthetic fibers appear to cause irritation and trigger symptoms in some people.
Environment and Eczema
There are also environmental factors that tend to be much harder to avoid. The weather itself can be an eczema trigger; specifically, cold and dry air, or very humid air, can lead to flares in susceptible folks.
Indoor air quality also plays a role, as house dust mites, mold, and pollen are all potential triggers. And if you have a furry friend living with you, that furry friend’s fur may not be much of a friend if you’re prone to dermatitis.
Indoor air can also be compromised by gas stoves, furniture off-gassing, construction materials, paints, and anything else that releases volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
The category of exposure that you may have the least control over is outdoor air pollutants. Chemicals from car exhaust, power plants, cigarette smoke, and even wildfires can all impair your skin’s ability to make healthy oils, leaving skin more easily irritated.
Food and Eczema
As we’ve seen, there’s a correlation between eczema and food allergies. Researchers estimate that up to 30% of children with eczema also have a food allergy — the most common ones being milk, egg, soy, peanut, tree nuts, wheat, fish and shellfish, and/or sesame.
Roughly the same percentage of adult eczema sufferers will also develop a food allergy in their lives, and experience symptoms such as hives, itching, difficulty breathing, or intestinal distress immediately after eating a specific type of food.
Interestingly, a distinct type of atopic dermatitis seems to have a direct link to food allergies right from the start. Children with this condition tend to show skin irregularities all over, not just in areas with active lesions.
However, in a broader sense, allergy specialists often view atopic dermatitis as an initial stage in the sequence known as the “atopic march.” This term describes a common pattern in some children, where atopic dermatitis evolves into food allergies and may even further develop into respiratory allergies or allergic asthma.
[Find out more about food allergies and what you can do about them.]
Can a Plant-Based Diet Help with Eczema?
Unlike medical specialties like cardiology and endocrinology, dermatology hasn’t yet acknowledged the potential health benefits of a plant-based diet. A 2022 review article noted that dermatologists typically advise against plant-based diets.
To be fair, there aren’t many studies that look specifically at the relationship between plant-based diets and eczema. We’ve seen a few anecdotal reports, which should not be dismissed just because they aren’t randomized controlled clinical trials. However, we do have some evidence suggesting that plant-based diets may help with eczema.
- A 2018 study asked 169 atopic dermatitis patients what changes they were making in their diets to treat their eczema, and whether their symptoms were improving. The greatest benefits were reported in those who added vegetables, especially organic ones, to their diets.
- A case study published in 2020 shared the story of a four-year-old patient with severe, persistent eczema. Ten days after the little girl was placed on a dairy-free elimination diet, her symptoms had improved by 76%. By the end of four months, she was in remission from eczema symptoms.
- Another study from back in 2001 took 20 eczema patients and put them on a strict plant-based diet. After just two months, they showed reduced markers of inflammation and immune response and a dramatic reduction in symptoms.
- And a 2021 Greek study on adolescents found that the more fruit, vegetables, and legumes they ate per week, the less they suffered from all atopic diseases, including eczema, allergic rhinitis (inflammation of the nasal cavities, and not a fear of rhinoceroses), and asthma.
- Interestingly, eating a plant-based diet during pregnancy may also lower the odds of an infant having eczema in their first year of life, according to a 2020 study.
There’s clearly much more research on eczema and plant-based diets that’s necessary. But we do know that plant-based diets contain many foods and compounds that are helpful for skin health, the immune system, and combating inflammation. They also generally eliminate some common food triggers and allergens, such as dairy, eggs, and shellfish. And whole food, plant-based diets also cut out processed foods, which are pro-inflammatory.
Food and Nutrients That May Help with Eczema
In general, diets rich in anti-inflammatory and antioxidant-rich foods may decrease inflammation and improve antioxidant status, thus positively affecting skin health. And probiotic and prebiotic foods, including fermented foods and those high in fiber, can also support a healthy gut microbiome and a balanced immune system — which may help improve eczema symptoms. These are just some of the nutrients and foods that help eczema go away.
Fermented Foods and Eczema
Fermented foods such as sauerkraut, kimchi, tempeh, and plant-based yogurt are not only high in antioxidants, they also deliver lactic acid-producing bacteria (LABs). The LABs support the “good” populations of gut bacteria and also improve local and systemic immunity.
Researchers surveyed 9,763 Korean adults in 2012–13 and found that those consuming large amounts of fermented foods (defined as eating fermented foods an impressive 92+ times per month!) had less atopic dermatitis than those who weren’t as committed to those foods.
For more on fermented foods, read our article: Fermented Foods: What are they, and how can they boost your health?
Fiber and Eczema
If you think of your gut as a party for probiotics, then dietary fiber is their all-you-can-eat buffet. Fermented foods, high in probiotics, are essentially the life of the party — but they can’t sustain themselves without a steady supply of dietary fiber — their version of party food.
In 2021, a group of Korean party planners — I mean, researchers — found that the more fiber-filled buffet options people had (i.e., the more dietary fiber they consumed), the less they had to worry about uninvited guests like eczema, asthma, and allergic rhinitis.
Fast-forward to 2022: A team of international researchers discovered the magic trick that happens when gut bacteria hit the fiber buffet hard. The short-chain fatty acids they produce can boost the bouncer at the door (the strength of the outer skin barrier), reducing the chances of allergens and related diseases crashing the party early.
Fiber-rich foods include all the usual suspects: legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, fruits, and veggies. Essentially, everything you’d find at a whole food, plant-based diet party — which sounds like a bash your gut would definitely want to RSVP to!
For more on why fiber is good for you, the best kinds, and the best sources, see our article, here.
Omega-3 and Eczema
In the modern industrialized diet, there’s a huge imbalance between the intake of omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids, with the former being consumed in much larger quantities than the latter.
Research shows that excess omega-6 is a risk factor for eczema, while omega-3 appears to inhibit an over-the-top immune response, such as cytokine production that can trigger inflammation of the skin.
A 2021 overview article in the International Journal of Molecular Sciences suggests that balancing the omega-6 GLA with omega-3 fatty acids may inhibit inflammatory responses, with positive effects on skin conditions such as eczema, psoriasis, and acne.
High omega-3 foods include flaxseeds, chia seeds, hemp seeds, walnuts, and certain forms of algae. And many vegan omega-3 supplements, like this one by Complement, are produced from algal oil.
For more on why omega-3s are important — and what the best sources are for your health — see our article here.
Vitamin D and Eczema
Vitamin D may also play an important role in easing or suppressing eczema symptoms. A 2016 meta-analysis found four randomized controlled trials that, taken together, suggest that vitamin D supplementation could safely reduce eczema symptom severity.
A 2019 meta-analysis found lower vitamin D levels in eczema patients than in healthy controls. And it highlighted three interventions in which vitamin D supplementation reduced eczema severity.
However, a 2023 meta-analysis argued that vitamin D didn’t improve eczema across the board, and that it appeared to make a positive difference in adults but not in children.
The confusion may arise from the question of whether the relationship between vitamin D levels and atopic dermatitis is causal, and if so, in which direction. That is, does low vitamin D increase the risk of eczema, or does having eczema decrease vitamin D levels, perhaps by compromising the ability of the skin to synthesize the vitamin from sunlight — or perhaps because eczema sufferers are less likely to expose their skin to the sun?
If you aren’t getting sufficient vitamin D via sun exposure, there are some foods that can deliver the nutrient, including fortified plant-based milk and orange juice, and UV-exposed mushrooms. There are also supplemental forms of vitamin D, like this highly bioavailable liposomal version from our friends at Purality Health.
For more on vitamin D, including how much you need and how to get enough, see our article, here.
Vitamin E and Eczema
Vitamin E is a powerful antioxidant and has been shown to reduce inflammatory compounds in patients with atopic conditions, including eczema.
A 2015 randomized trial gave participants either 400 IU of oral vitamin E or a placebo for four months. And the researchers found that the vitamin significantly reduced itching and the extent of skin lesions.
A 2020 review of the full medical literature on the relationship between vitamin E and eczema concluded that supplementation “has great potential as an adjunctive treatment for AD (Atopic Dermatitis) owing to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory bioactivities.”
While 400 IU is considered a safe dose, there are risks of getting too much vitamin E from supplements. You may not need to supplement if you focus on foods naturally high in vitamin E. These include nuts, seeds, avocado, mango, bell pepper, and leafy greens.
For more on vitamin E, including why it’s important and the best sources, see our article, here.
Eczema-Friendly Recipes
If you (or anyone you love) suffer from eczema and are inspired to see if a healthy diet can help, these eczema-friendly recipes are sure to make it a tasty transition.
Incorporating at least one of these recipes a week just might do wonders for the overall health of your immune system, microbiome, and skin.
Each recipe features foods packed with fiber and powerful, anti-inflammatory nutrients that could improve eczema symptoms. They’re also free of many of the most irritating food allergens, such as dairy, eggs, and shellfish.
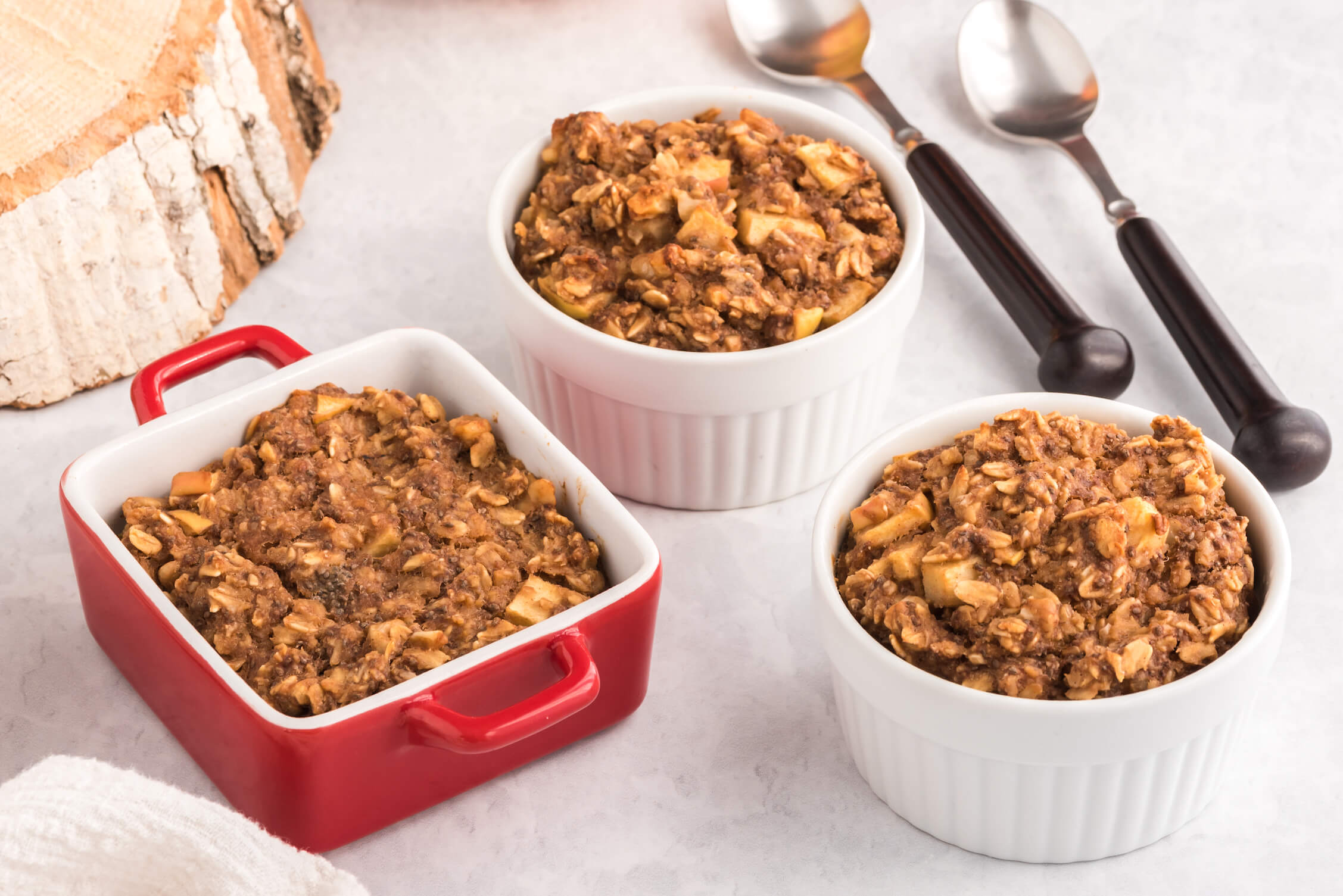
1. Apple Walnut Oatmeal Bake
This comforting dish is full of healthful, anti-inflammatory ingredients to help soothe your skin during an eczema flare. Rich in calming and fiber-rich oats, omega-3-packed chia and walnuts, and vitamin D-fortified plant-based milk (if you use fortified plant milk), you could call this a breakfast made for healthy skin!
2. Kelp Salad with Baked Tempeh and Kimchi Miso Dressing
Kelp Salad with Baked Tempeh and Kimchi Miso Dressing brings together highly nutritious fermented foods, including tempeh and kimchi, which support a healthy microbiome. Helping supply your gut with the good bacteria it needs may reduce incidences of eczema flares.
This flavorful salad also has omega-3 fatty acids from the hemp seeds, calcium from the tahini, iodine from the kelp, iron from the beets, and zinc from the pumpkin seeds. You’ll cover lots of your nutritional bases with this one plant-powered salad!
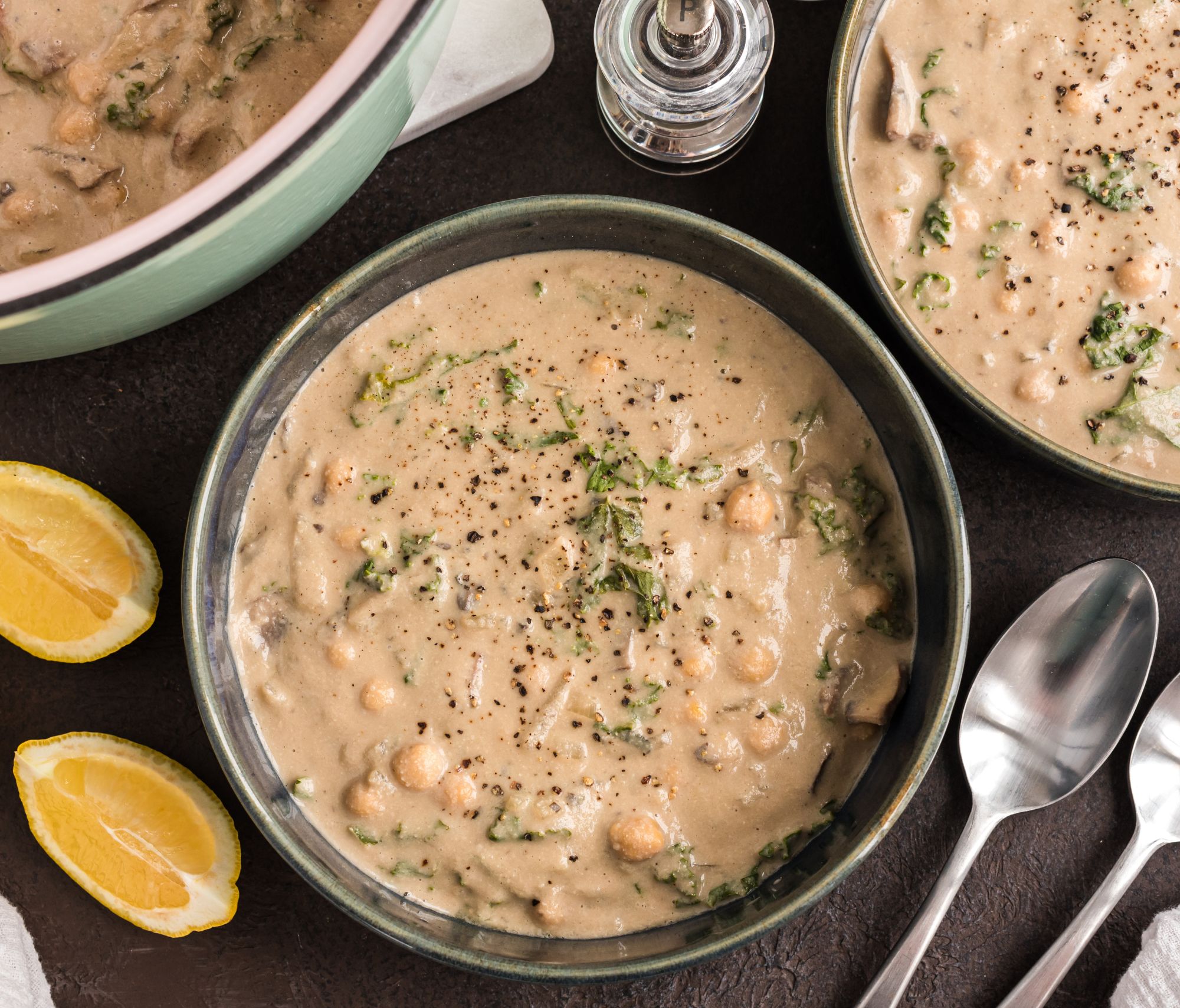
3. Creamy Mushroom Soup with Chickpeas and Kale
Creamy Mushroom Soup with Chickpeas and Kale is a super cozy bowl of nourishing plants that provides comfort in more ways than one. In addition to the soup’s mouthwatering umami flavors from mushrooms, chickpeas, kale, and cashews, it packs a nutrient-dense punch! It’s a potent source of vitamin E, vitamin D (depending on the amount of sun exposure your mushrooms get), fiber, and protein, just to name a few. This soup is a delicious way to nourish your skin barrier and gut microbiome.
Reach for Plants to Support Your Skin from the Inside Out!
While scientific evidence supporting dietary interventions for eczema is still limited, the link between diet and overall skin health is strong enough that you may want to prioritize a healthy, plant-based diet as a first-line treatment strategy. A diet rich in nutrient-dense fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds holds promise in providing essential nutrients, reducing inflammation, and supporting skin barrier function.
Prioritizing skin-supporting nutrients, such as omega-3 fatty acids, fiber, probiotics, and vitamins E and D, could play a vital role in managing eczema.
The benefits of plant-based eating also come from what the diet eliminates. Avoiding potential allergens or trigger foods and pro-inflammatories, such as dairy and processed foods, could help in many cases.
Reducing stress and exposure to environmental toxins can also play a meaningful role in reducing eczema symptoms. In severe cases, consulting a health care professional may be necessary, to develop an individualized approach tailored to specific needs and preferences.
Tell us in the comments:
-
Do you have eczema? If so, do you know what triggers it for you?
-
Have any diet and lifestyle strategies reduced flares and lessened symptoms?
-
Have you tried eliminating certain foods and increasing others?
Featured Image: iStock.com/nensuria